In IB Physics First Assessment 2016, modelling a gas is a subtopic of Topic 3 thermal physics. This subtopic has the following understandings associated with it.
- Pressure
- Equation of state for an ideal gas
- Kinetic model of an ideal gas
- Mole, molar mass and the Avogadro constant
- Differences between real and ideal gases
In this part of the analysis, I am particularly interested in “What is the frequency distribution of the questions concerning modelling a gas understandings?”
Frequency distribution of questions by modelling a gas understandings for HL
Between 1999-2023
For the entire dataset for HL, more than two-thirds of the questions came from the equation of state for an ideal gas understanding. The kinetic model of an ideal gas accounted for about one-fifth of the questions. Mole, molar mass, and Avagadro constant and pressure were rarely assessed.
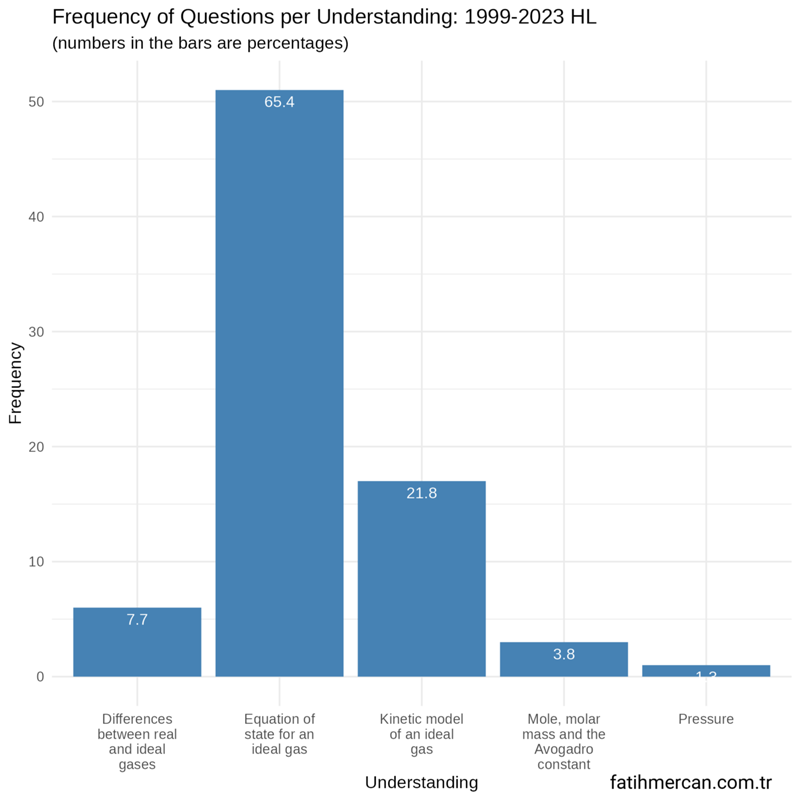
Figure 1
Between 2016-2023
Between these years for HL, the distribution is similar to the entire dataset.
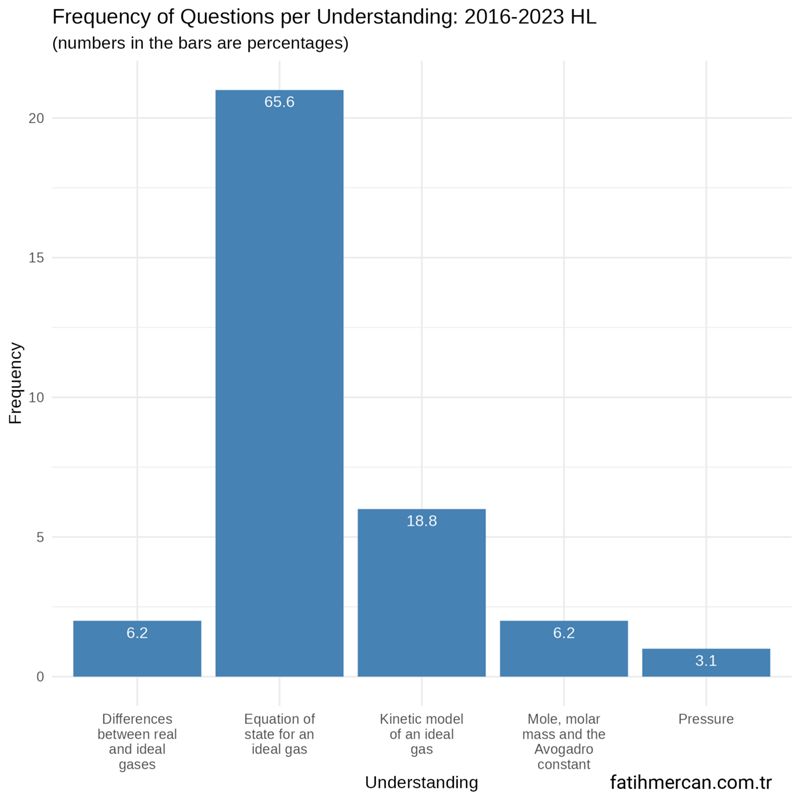
Figure 2
Frequency distribution of questions by modelling a gas understandings for SL
Between 1999-2023
For the entire dataset for SL, the shape of the distribution is similar to HL. Again, more than half of the questions came from the equation of state for an ideal gas. More than a quarter of questions came from the kinetic model of an ideal gas understanding.
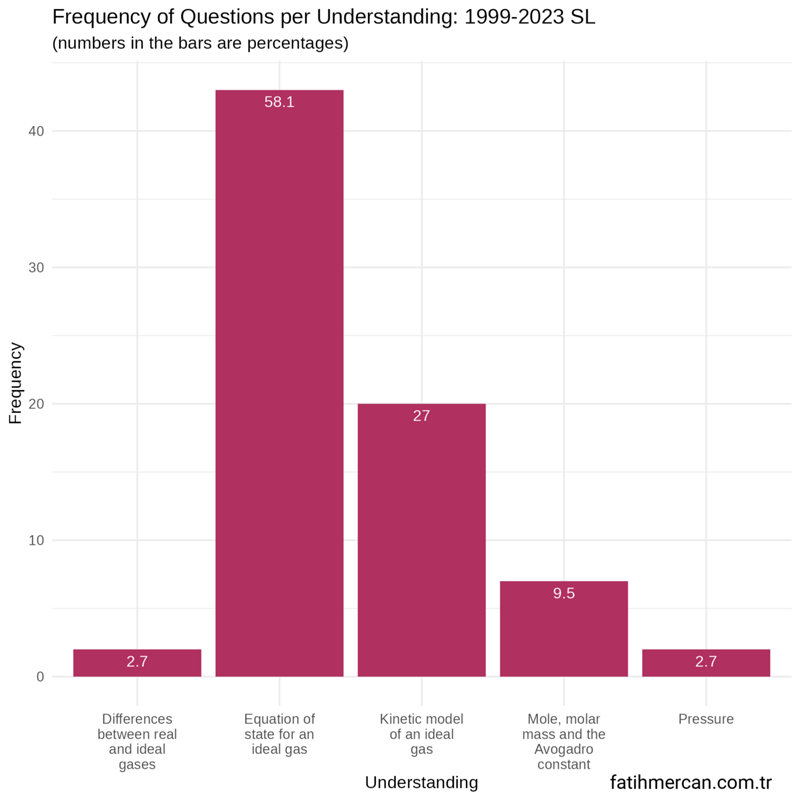
Figure 3
Between 2016-2023
Between these years, the distribution is very similar to the entire dataset for SL. The equation of state for an ideal gas and kinetic model of an ideal gas account for nine-tenths of the questions. The remaining three understandings are rarely assessed.
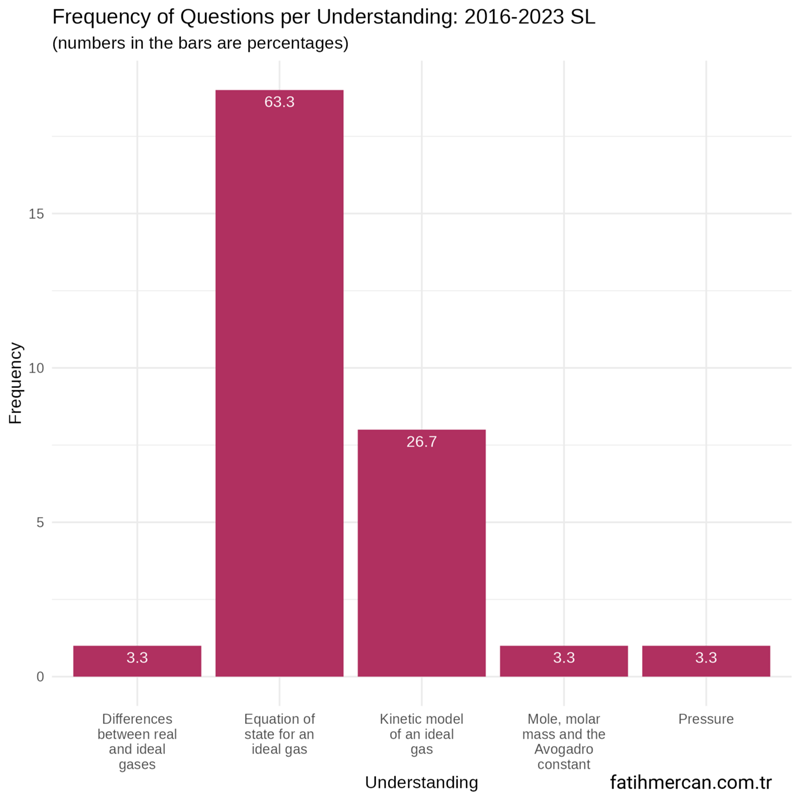
Figure 4
Where to go from here?
You may want to check out the other related subtopics:
- Thermal concepts
- Modeling a gas
If you are interested in more detailed analyses of the topics:
- Measurement and uncertainties
- Mechanics
- Thermal physics
- Waves
- Electricity and magnetism
- Circular motion and gravitation
- Atomic, nuclear and particle physics
- Energy production
- Wave phenomena
- Fields
- Electromagnetic induction
- Quantum and nuclear physics
This work/product/service has been developed independently from and is not endorsed by the International Baccalaureate Organization. International Baccalaureate, Baccalauréat International, Bachillerato Internacional and IB are registered trademarks owned by the International Baccalaureate Organization.
